How HPMC Improves Water Retention Efficiency and Reduces Moisture Loss in Cement-Based Systems
Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose (HPMC) plays a vital role in improving water retention efficiency in cement-based systems such as plastering mortar, tile adhesive, self-leveling compounds, and masonry mortar. During mixing, HPMC rapidly dissolves in water and forms a uniform, three-dimensional polymer network. This network increases the viscosity of the fresh mortar, effectively binding free water within the system and slowing down moisture migration.
By reducing water evaporation and absorption into porous substrates, HPMC ensures sufficient water is available for complete cement hydration. Proper hydration is critical for strength development, adhesion performance, and long-term durability. Without adequate water retention, cement-based materials may experience rapid drying, leading to weak bonding, poor surface quality, and early-age cracking.
HPMC also acts as a protective colloid, stabilizing the distribution of cement particles and fine fillers. This stabilization minimizes segregation and bleeding, further reducing water loss during application. In addition, improved water retention extends the open time of mortar, allowing applicators more flexibility for adjustment and finishing, especially under hot, dry, or windy conditions.
HPMC significantly enhances the consistency and reliability of cement-based systems by controlling moisture behavior. Its water retention capability not only improves workability but also ensures optimal hydration, resulting in stronger, smoother, and more durable construction materials.
The Influence of HPMC on Hydration Stability, Open Time, and Workability Control
Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose (HPMC) has a significant influence on hydration stability, open time, and overall workability in cement-based systems. Once dispersed in water, HPMC forms a stable polymer film that regulates water movement within the mortar. This controlled moisture environment supports uniform cement hydration, preventing localized drying or premature setting that can compromise mechanical performance.

By retaining water around cement particles, HPMC slows down the initial hydration rate in a controlled manner. This helps stabilize setting behavior, reducing the risk of flash set while maintaining sufficient strength development. As a result, the hydration process becomes more predictable and consistent, even under challenging application conditions such as high temperatures or absorbent substrates.
HPMC also effectively extends open time, allowing installers more time for spreading, positioning, and adjustment. This is especially important for tile adhesives and plastering mortars, where adequate open time directly affects bonding quality and installation efficiency. At the same time, HPMC improves workability by enhancing mortar cohesion and smoothness. The material becomes easier to apply, spread, and finish, with reduced stickiness or slump.
HPMC provides a balanced combination of hydration control, extended open time, and stable workability, ensuring reliable application performance and improved construction quality.
HPMC Water Retention Effects on Adhesion Strength, Surface Quality, and Crack Prevention
The water retention capability of Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose (HPMC) has a direct and positive impact on adhesion strength, surface quality, and crack prevention in cement-based materials. By effectively retaining moisture within the fresh mortar, HPMC ensures that cement hydration proceeds fully and uniformly. Complete hydration promotes the formation of a dense cement matrix, which is essential for strong bonding to substrates such as concrete, masonry, and tiles.

Improved water retention also enhances adhesion by preventing rapid water loss to porous substrates. When sufficient moisture remains at the interface, cement particles can properly hydrate and interlock with the substrate surface, resulting in higher bond strength and reduced risk of debonding or hollowing.
In terms of surface quality, HPMC helps produce smoother, more uniform finishes. By minimizing bleeding, segregation, and premature drying, it reduces surface defects such as pinholes, dusting, and uneven textures. The mortar remains workable for longer, allowing better leveling and finishing.
HPMC plays a crucial role in crack prevention. Controlled moisture release reduces shrinkage stress during early curing, lowering the likelihood of plastic shrinkage cracks. Overall, HPMC water retention contributes to stronger adhesion, superior surface appearance, and long-term durability of cement-based systems.
Selecting the Right HPMC Grade to Optimize Water Retention for Different Formulations and Application Conditions
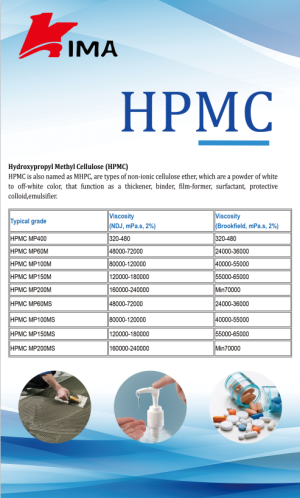
Choosing the appropriate Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose (HPMC) grade is critical to achieving optimal water retention in various cement-based formulations, as different grades exhibit distinct viscosity levels, substitution types, and molecular weights. High-viscosity grades are ideal for applications requiring maximum water retention, such as plastering mortars and self-leveling compounds applied in hot or dry conditions. These grades form a robust polymer network that slows water evaporation, extends open time, and maintains consistent workability.

Medium-viscosity HPMC grades are suitable for tile adhesives, masonry mortars, and repair mortars, where a balance between water retention, spreadability, and ease of application is needed. These grades provide sufficient moisture control without overly thickening the mortar, ensuring proper substrate wetting and adhesion. Low-viscosity HPMC grades are often used in lightweight or fine-fill formulations, where excessive viscosity could hinder leveling and application precision.
Environmental and substrate conditions also influence grade selection. In high-temperature or low-humidity environments, higher viscosity or higher substitution HPMC ensures prolonged moisture retention, whereas standard conditions may require lower viscosity grades to maintain workability.
By carefully selecting the HPMC grade based on formulation type, substrate, and application environment, manufacturers and applicators can optimize water retention, improve cement hydration, enhance adhesion, and reduce cracking, resulting in high-performance, durable, and aesthetically smooth cement-based materials.
 English
English 日本語
日本語 français
français Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español italiano
italiano русский
русский português
português العربية
العربية Türkçe
Türkçe Nederland
Nederland







