Redispersible polymer powders (RDP) are free-flowing, white powders obtained by spray-drying polymer emulsions. These powders are specially formulated to redisperse in water, regenerating the original polymer emulsion with properties very close to the liquid form. RDP are widely used as key additives in modern dry-mix construction materials due to their ability to enhance workability, flexibility, adhesion, and durability.

Chemical Composition and Types
RDP are typically composed of:
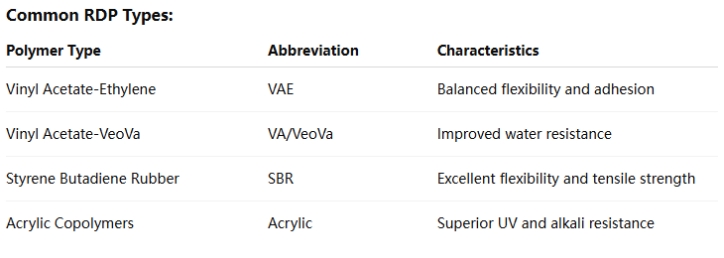
Polymer Base: The core component of RDP, usually vinyl acetate-ethylene (VAE), vinyl acetate-vinyl versatate (VA/VeoVa), styrene-butadiene (SBR), or acrylic-based copolymers.
Protective Colloid: Often polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), used as a stabilizer and to prevent the particles from coalescing during drying and storage.
Anti-caking Agent: Typically fine mineral fillers like kaolin or calcium carbonate are added to ensure the powder remains free-flowing and easy to handle.
Production Process
The production of RDP involves the following stages:
Emulsion Polymerization: The base polymer is synthesized in an aqueous medium.
Spray Drying: The polymer emulsion is atomized and dried in a hot air stream. During this process, protective colloids help encapsulate polymer particles, forming a powder.
Packaging: After drying and sieving, the RDP is collected and packed in moisture-proof bags to ensure stability.
When reintroduced to water, the RDP quickly forms a stable dispersion, similar to the original latex, thus regaining its properties.
Mechanism of Action
Upon mixing RDP with water and cementitious or gypsum-based formulations:
The powder redisperses into discrete polymer particles.
These particles coalesce during the curing process, forming a continuous film throughout the matrix.
The film binds the solid components (like sand and cement) and imparts flexibility and adhesion.
This film formation is responsible for most of the improved mechanical and durability properties of modified mortars.
Key Properties and Benefits
4.1. Adhesion Improvement
RDP enhances bonding between mortar and substrates (e.g., concrete, masonry, wood, old tiles). This is crucial for applications like tile adhesives and repair mortars.
4.2. Flexibility and Crack Resistance
The polymer film can absorb strain and bridge microcracks, making mortars more durable under mechanical stress or thermal expansion.
4.3. Water Retention
RDP contribute to better water retention, ensuring sufficient curing time, reducing the risk of early cracking, and improving final strength.
4.4. Workability
Mortars with RDP exhibit improved rheology, smoother application, and better trowelability.
4.5. Abrasion and Weather Resistance
RDP improve surface hardness, resistance to abrasion, freeze-thaw cycles, and long-term weather exposure.
Applications in Construction
5.1. Tile Adhesives and Grouts
RDP enable strong bonding to tiles and substrates, including non-absorbent materials. They also improve open time and flexibility.
5.2. Self-Leveling Compounds
In floor leveling systems, RDP enhance flow, prevent segregation, and improve surface strength.
5.3. External Thermal Insulation Composite Systems (ETICS)
Used in base coat mortars and adhesives, RDP offer improved bonding to insulation boards and substrate, along with impact resistance.
5.4. Waterproofing Mortars
By forming flexible films, RDP contribute to the water impermeability of mortars applied in bathrooms, roofs, and basements.
5.5. Repair Mortars
In concrete repair systems, RDP enhance bonding to old concrete and impart durability under harsh conditions.
5.6. Render and Skim Coats
Improved adhesion, workability, and crack resistance help deliver long-lasting decorative and protective layers.
Dosage and Compatibility
Typical dosage ranges from 1% to 5% by weight of dry mortar mix, depending on the application.
RDP are compatible with other additives like cellulose ethers, superplasticizers, defomers, and hydration control agents.
Excess dosage may lead to delayed setting or reduced compressive strength.

Environmental and Handling Considerations
Shelf Life: RDP should be stored in dry conditions. Exposure to moisture can cause premature caking or degradation.
Health and Safety: Generally non-toxic, but protective measures (masks and gloves) are advised during handling to avoid inhalation or skin contact.
Eco-Friendliness: Some modern RDP are formulated with low VOC content, making them suitable for green building certifications (e.g., LEED).
Future Trends and Innovations
With growing demand for sustainable and high-performance construction materials, RDP are evolving in several directions:
Bio-based polymers as environmentally friendly alternatives.
Modified chemistries for better performance in extreme climates.
Nano-enhanced RDP for improved adhesion and water resistance.
Integration into pre-packed dry mortars, enabling easy on-site mixing.
Redispersible polymer powders are indispensable components in modern construction chemicals, enabling superior performance of dry-mix products. Through their unique ability to enhance adhesion, flexibility, and durability, RDP contribute significantly to the quality and longevity of mortars, adhesives, and repair systems. As building standards and sustainability requirements continue to rise, the role of RDP in construction innovation will only grow further.
 English
English 日本語
日本語 français
français Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español italiano
italiano русский
русский português
português العربية
العربية Türkçe
Türkçe Nederland
Nederland






